Engineering & Technology
News
24 Feb 2023
Synthetic hydrogels were shown to provide an effective scaffold for neuronal tissue growth in areas of brain damage, providing a possible approach for brain tissue reconstruction.
23 Feb 2023
Scientists from Oil Crops Research Institute (OCRI) of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS), Anhui Agricultural University (Anhui, China), Newcastle University in Singapore, and Huizhou Comvikin Biotechnology Co., Ltd (Guangdong, China) have developed a green and efficient approach to synthesize highly liposoluble and antioxidant L-ascorbyl esters by immobilized lipases.
21 Feb 2023
An effective, stable solid-state electrochemical transistor has been developed, heralding a new era in thermal management technology.
17 Feb 2023
Tree rings forecast extreme weather in central Asia, Squid 🦑and chemistry make versatile hydrogels, James Webb telescope reveals the earliest galaxies & Reducing negative effects of screen time. Read all in the latest Editor's Choice. Plus our latest journalist resource "Experts for Media: Antimicrobial Resistance "🦠.
13 Feb 2023
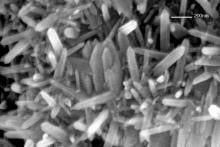
A research group from the Graduate School of Engineering at Osaka Metropolitan University has shown that 3C-SiC exhibits high thermal conductivity equivalent to the theoretical value, based on thermal conductivity evaluation and atomic-level analysis, for the first time. They demonstrated that a 3C-SiC film on silicon substrate had a high thermal conductivity and expect that fabricating large-diameter wafers can be achieved at a low cost. The discovery should lead to improved heat dissipation in everyday electronic devices.
09 Feb 2023
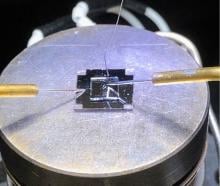
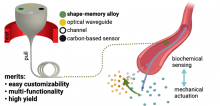
A research team led by an associate professor at Tohoku University has developed a microscopic fiber equipped with actuators and biochemical sensors. The breakthrough could be used to develop smart catheters and lead to further advancement in robotics.
07 Feb 2023
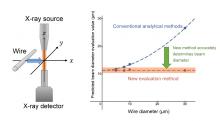
A research group at Osaka Metropolitan University has derived a new evaluation method for the measuring the size X-ray microbeams (diameter) through mathematical analysis. The group then verified the validity of the mathematically derived evaluation method by measuring the diameter of X-ray microbeams using metal wires of various diameters with an X-ray fluorescence analysis system for small areas and found that it was possible to calculate the beam diameter more accurately than the previous conventional evaluation method.
05 Feb 2023
Scientists from two Asian universities, namely Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM) and Newcastle University in Singapore, have completed a study to understand how the mechanical behaviour of carbon fibre reinforced epoxy composite laminates could be compromised by moisture seepage.
31 Jan 2023
The study is an important step towards the understanding of long-term changes in the water cycle and will aid in more informed decisions when assessing and managing regional water systems.
26 Jan 2023
Scientists at Malaysia’s IIUM are helping small and medium business owners in Sarawak to use technology to cut costs and improve marketing.
26 Jan 2023
Students at IIUM are leaving the confines of their university campus to transfer the knowledge they gain to communities all over Malaysia.
24 Jan 2023
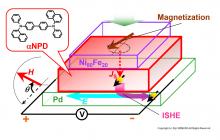
A research group, at the Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Engineering, has succeeded in measuring spin transport in a thin film of αNPD molecules—a material well-known in organic light emitting diodes—at room temperature. They found that this thin molecular film has a spin diffusion length of approximately 62 nm, a length that could have practical applications in developing spintronics technology. In addition, while electricity has been used to control spin transport in the past, the thin molecular film used in this study is photoconductive, allowing spin transport control using visible light.
20 Jan 2023
Overeating mechanism: why "eating just one chip"🍟 is impossible, Measuring hidden energy of gamma-ray bursts, Marine species that can adapt to ocean acidification & A rough start can lead to a strong bond, Read all in our first Editor's Choice of 2023. Plus our interview on what dengue vaccine approval in EU💉means for global dengue protection.
19 Jan 2023
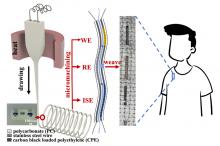
Imagine if your t-shirt could take your sweat and analyze it for health abnormalities. Well, this is much closer to reality after a recent breakthrough by a research group led by a Tohoku University assistant professor. The group created the first microelectronic fiber with microscopic parameters that is capable of analyzing electrolytes and metabolites in sweat.
09 Jan 2023
Scientists from five Asian universities, namely Vellore Institute of Technology (VIT), Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM), Charles Darwin University, National Defence University of Malaysia, and Newcastle University in Singapore have completed and published a comprehensive survey of the complex nature of natural fibre reinforcing composite materials.
06 Jan 2023
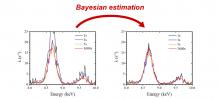
A research group at Osaka Metropolitan University has succeeded in significantly reducing the measurement time of a glass standard sample by applying Bayesian estimation to X-ray fluorescence analysis. The ability to perform rapid non-contact elemental analysis in a nondestructive manner could lead to the widespread use of this technique in many fields, including the analysis of moving industrial products and waste materials while being carried on conveyor belts.
05 Jan 2023
Researchers at The University of Tokyo simulate the phase separation of self-spinning particles, and show that the process differs from other unmixing processes, which may shed light on the organization of bacteria and other organisms
29 Dec 2022
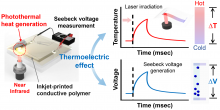
- A joint research team led by DGIST Professor Kang Hong-gi and KIST Dr. Chung Seung-jun develops high-speed powerless photothermal effect temperature sensor technology using a transparent polymer thermoelectric material printing process
- Opens up the possibility of direct high-resolution measurement of nano-photothermal phenomenon without interference of light, proposed for brain stimulation, cancer treatment, and ultra-fast PCR, etc.... Published online in ‘Materials Horizons’ in October
22 Dec 2022
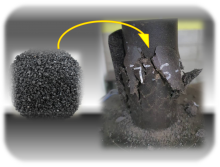
Wearing face masks has been recognised as one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of COVID-19, even in its coming endemic phase. Apart from the conventional function of masks, the potential for smart masks to monitor human physiological signals is being increasingly explored. A research team led by the City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently invented a smart mask, integrating an ultrathin nanocomposite sponge structure-based soundwave sensor, which is capable of detecting respiratory sounds of breathing, coughing and speaking.
15 Dec 2022
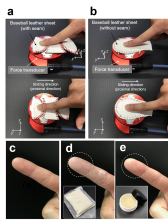
In baseball, even the smallest detail can tip the scales in favor of the batter or the pitcher. A recent publication has highlighted how rosin powder helps maintain a more constant friction when pitching, something that could bring about a fairer playing field in Major League Baseball.
15 Dec 2022
A research team led by the University of Hong Kong (HKU) and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory has invented an all-water robotic system that resolves the constraints of bio-inspired robots through revolutionary scientific advances.
15 Dec 2022
Understanding how bats tolerate viral infections, Material separates water from...water, The virtual sense of touch polished to next level and COVID-19 negatively impacted early-careers and female researchers. Read all in the December's Editor's Choice.
14 Dec 2022
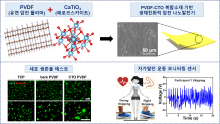
- DGIST Joint Team of Professors Kim Hoe-joon and Hong Seon-ki developed high-efficiency piezoelectric energy harvesting technology using materials harmless to humans
- Attachable to body, generates energy and diagnoses exercise posture... Published in the November issue of ‘Nano Energy’
13 Dec 2022
Researchers at The University of Tokyo develop a simple but effective method of bonding polymers with galvanized steel, a material ubiquitous in the automobile industry, to cheaply and easily create a lightweight and durable product.
09 Dec 2022
Scientists from Universiti Teknologi Malaysia have reported a novel way to produce reinforced concrete materials using tin slag aggregates, which is a by-product of the smelting process. This way of producing concrete enables tin slag to become a useful material, as well as reducing the amount of natural resources used, which in turn contribute to reducing carbon footprint in the construction industry.
09 Dec 2022
A new coating for tiny packages called liposomes could allow them to carry vaccines and drugs into and around the body more safely.
07 Dec 2022
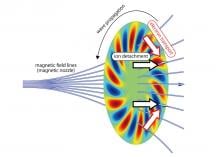
Magnetic nozzle plasma thrusters are thought of as the future of space travel. But one problem has hampered their development – plasma detachment. A recent study has shown that spontaneously excited plasma waves help magnetic nozzles overcome the plasma detachment problem, a rare instance of plasma instabilities having a positive effect on engineering.
02 Dec 2022
What if you could tell if your surroundings contained COVID-19 particles or droplets the moment they or you entered the vicinity? This is now closer to reality. A research group has engineered a battery-less, self-powering device that can wirelessly transmit the detection of coronavirus in the air.
02 Dec 2022
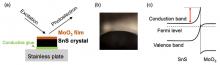
Tin sulfide (SnS) solar cells have shown immense promise in the rush to develop more environmentally friendly thin-film solar cells. Yet for years SnS solar cells have struggled to achieve a high conversion efficiency. To overcome this, a SnS interface exhibiting large band bending was necessary, something a research group has recently achieved.
Events
Sorry, nothing coming up for this discipline
- « first
- ‹ previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Giants in history
Sorry, nothing coming up for this discipline