Biology
News
13 Oct 2023
A new amphipod species thrives at record temperatures in nearby hot spring pools of an ancient Inca city, defying norms for these typically cold-dwelling animals. Unraveling its key adaptations can give clues for the survival of other freshwater creatures in our warming world.
05 Oct 2023
Hunting for supermassive black holes, Coastal survival at risk, Calcium and dead cell clean-up, Two naps are better than one & Pineapple leaf prosthetics. Read all in the latest Editor's Choice.
05 Oct 2023
The finalists in the Applied Microbiology International Product of the Year Award 2023 have been announced. The awards promote the research, groups, projects, products and individuals who are shaping the future of applied microbiology.
05 Oct 2023
Acoels have been found to host a wide diversity of symbiotic, photosynthetic microalgae.
05 Oct 2023
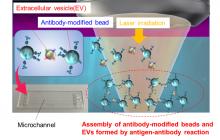
Osaka Metropolitan University researchers have used the power of laser light to accelerate the reaction between cancer cell-derived extracellular vesicles—a kind of nanoparticle—and antibody-modified microparticles. The three-dimensional structure of the resulting aggregates was then analyzed using a confocal optical system. The results demonstrated the ability to measure, within 5 minutes, approximately 1,000 to 10,000 nanoscale EVs contained in a 500 nL sample.
29 Sep 2023
The authors discovered a shorter isoform of Rubicon called RUBCN100, which enhances autophagy in B cells.
29 Sep 2023
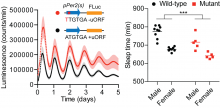
The authors identified a structure in the circadian mRNA Period2 that affects the sleep-wake cycle. The results indicate how translation and post-transcriptional processes influence the body’s internal clock and its impact on sleep patterns.
15 Sep 2023
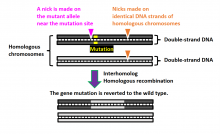
Researchers led by Osaka University developed a novel genome editing technique known as NICER, which results in significantly fewer off-target mutations than CRISPR/Cas9 editing. The technique uses a different type of enzyme that makes single-stranded “nicks” in the DNA. Repair of these nicks is more efficient and accurate than repair of double-strand breaks caused by the current CRISPR/Cas9 editing. This technique represents a novel approach for the treatment of genetic diseases caused by heterozygous mutations.
15 Sep 2023
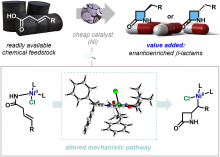
- Team led by DGIST Professor Seo Sang-won, in collaboration with IBS Molecular Activation Catalysis Research Team, significantly simplifies complex antibiotic synthesis processes
- Synthesizing pharmaceutical raw materials with a 700 times higher market value from hydrocarbons using economical catalysts
- Article published in Nature Catalysis, the top international journal in chemistry
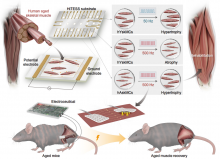
15 Sep 2023
This novel technology:
- provides potential treatment in relation to restoring aging muscle cells obtained from older adults and remedying sarcopenia in aging animals through bioelectric medicine
- presents a new paradigm for treating sarcopenia, for which no drugs are currently available to treat this condition
- has been reported in the internationally renowned academic journal, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS)
15 Sep 2023
- Research team led by Professor Minsik Kim at DGIST discovered the mechanism of autism spectrum disorder caused by the use of valproate in pregnant women through multi-institution joint research
- Published in the world-renowned journal “Experimental & Molecular Medicine”
15 Sep 2023
- Initial research findings from the project led by the Korea Environmental Industry & Technology Institute, focused on “Advancing Island Wildlife Materials.”
- Contributing to securing wildlife and constructing utility information big data.
14 Sep 2023
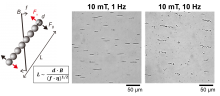
- Team led by Professor Choi Hong-Soo at DGIST enhances the effects of magnetic hyperthermia and particle penetration into cancer cells through the chain disassembly mechanism of magnetic nanoparticles induced by magnetic fields and magnetic propulsion.
- Expected to play a major role in targeted drug delivery for cancer treatment through research related to magnetic carriers.
- The research findings have been published in ACS Nano, a top-tier journal in the field of materials science.
14 Sep 2023
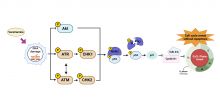
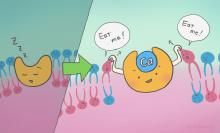
Scientists have found that extracellular calcium mediates the activation of a membrane protein that waves the flag signalling cell death
11 Sep 2023
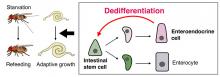
Researchers have unveiled an intriguing phenomenon of cellular reprogramming in mature adult organs, shedding light on a novel mechanism of adaptive growth. The study, which was conducted on fruit flies (Drosophila), provides further insights into dedifferentiation - where specialized cells that have specific functions transform into less specialized, undifferentiated cells like stem cells.
11 Sep 2023
Researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University have developed a measurement technique that rapidly measures the number of viable bacteria in food products. They have succeeded in drastically reducing the inspection time from 2 days to about 1 hour. With this technology, it will be possible to confirm food safety before shipment from factories and prevent food poisoning.
10 Sep 2023
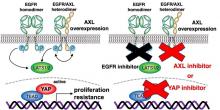
AXL and EGFR inhibitors combined hold promise in fighting certain head, neck, and lung cancers
08 Sep 2023
Capturing carbon dioxide, Shells go nuclear, Worms surf electric fields, Brain repair & Creating matter from light. Plus from our blog: Monitoring research for further impact. Read all in the latest Editor's Choice.
08 Sep 2023
Study addresses gaps in understanding of swine influenza A virus evolution and highlights need for early warning of disease emergence
05 Sep 2023
DishBrain reveals how human neurons work together to process information. Living model of brain could give insights into the mechanisms of how we understand and experience the world.
04 Sep 2023
In recent years, an emerging zoonotic pathogen called E. albertii, transmitted by wild animals such as raccoons, has garnered attention due to its remarkable similarities to several strains of Escherichia coli (E. coli), including O157, and its potential to cause severe illness, particularly in children. A research group at Osaka Metropolitan University has developed a novel culture medium that allows for the selective cultivation of E. albertii from raccoon fecal samples. This enabled the successful isolation of E. albertii even from samples with very low quantities of this bacterium. Their findings are expected to further elucidate the bacteriological characteristics of E. albertii and to contribute to the control of foodborne illnesses.
01 Sep 2023
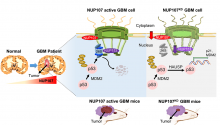
Researchers at Kanazawa University report in Cell Reports how alterations in the nuclear pores lead to the degradation of anti-tumor proteins.
31 Aug 2023
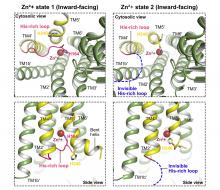
Roughly 10% of the proteins in our body rely on zinc. A group of researchers has unearthed the secrets behind a tiny but crucial protein that shuttles zinc ions within our bodies, offering a deeper understanding of how our cells maintain optimal health.
29 Aug 2023
A long-lived monocarpic species of bamboo, Phyllostachys nigra var. henonis, only flowers once every 120 years before it dies. The upcoming flowering event for this species does not bode well for its continued long-term survival, as most flowers are not producing viable seeds.
24 Aug 2023
Study suggests broad-spectrum vaccines with wide coverage necessary to achieve effective immunity against future, functionally-distinct variants.
23 Aug 2023
Researchers have identified a new pathway by which sugar is released by symbiotic algae. This pathway involves the largely overlooked cell wall, showing that this structure not only protects the cell but plays an important role in symbiosis and carbon circulation in the ocean.
21 Aug 2023
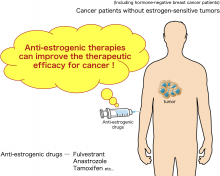
Anti-estrogenic therapies can suppress the growth of cancer that does not express estrogen receptors; when combined with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapies, they halt tumor progression in mice models.
19 Aug 2023
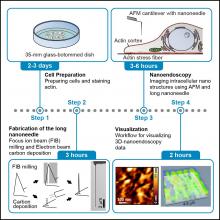
Researchers at Kanazawa University report in STAR Protocols procedural details and tips for nanoendoscopy-AFM, for capturing images of nanoscale structures inside living cells.
18 Aug 2023
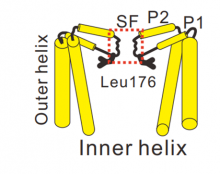
Researchers at Kanazawa University report in Nature Communications how calcium ions can block sodium ion channels located in cell membranes. Structural analysis and computer simulations made it possible to identify where and why calcium ions get stuck.
Events
Sorry, nothing coming up for this discipline
Researchers
Sorry, nothing coming up for this discipline
- « first
- ‹ previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
Giants in history
Sorry, nothing coming up for this discipline
- « first
- ‹ previous
- 1
- 2
- 3